Ask AI on The Internet
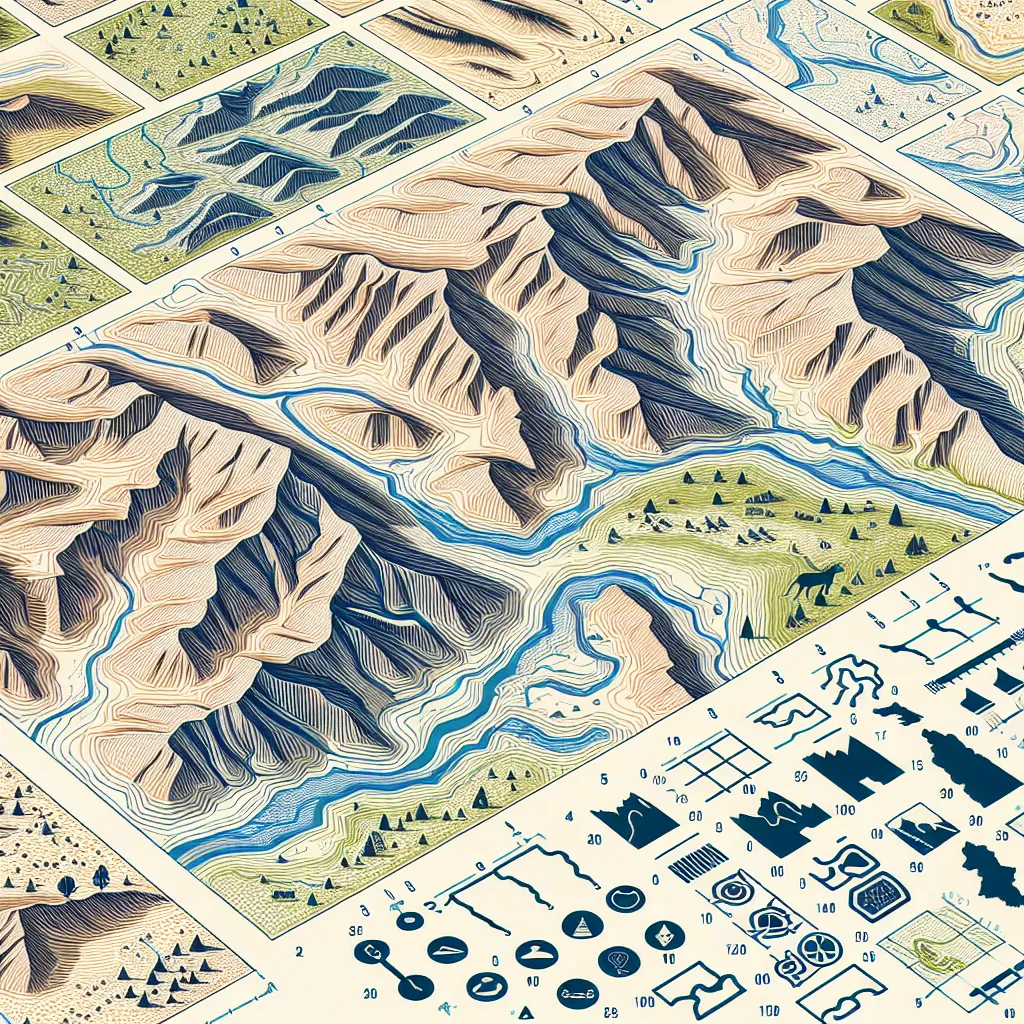
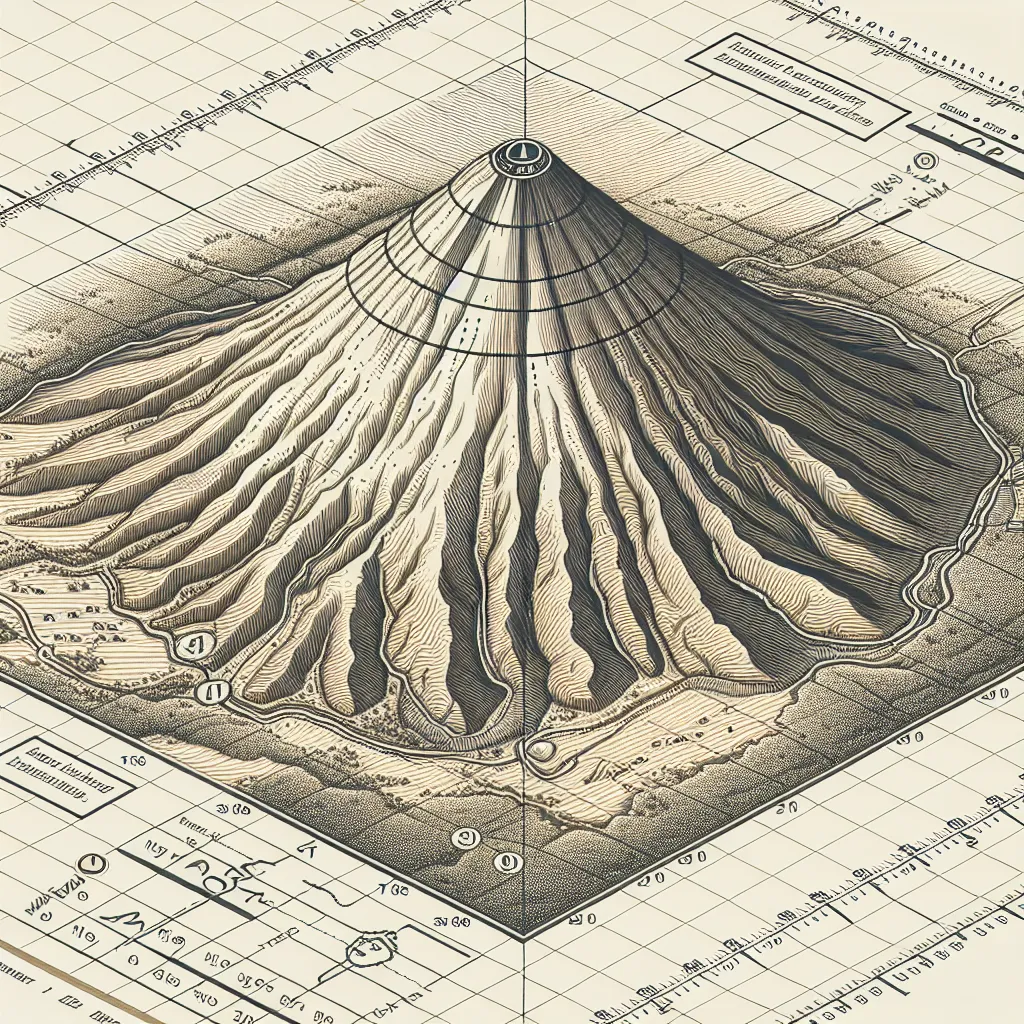
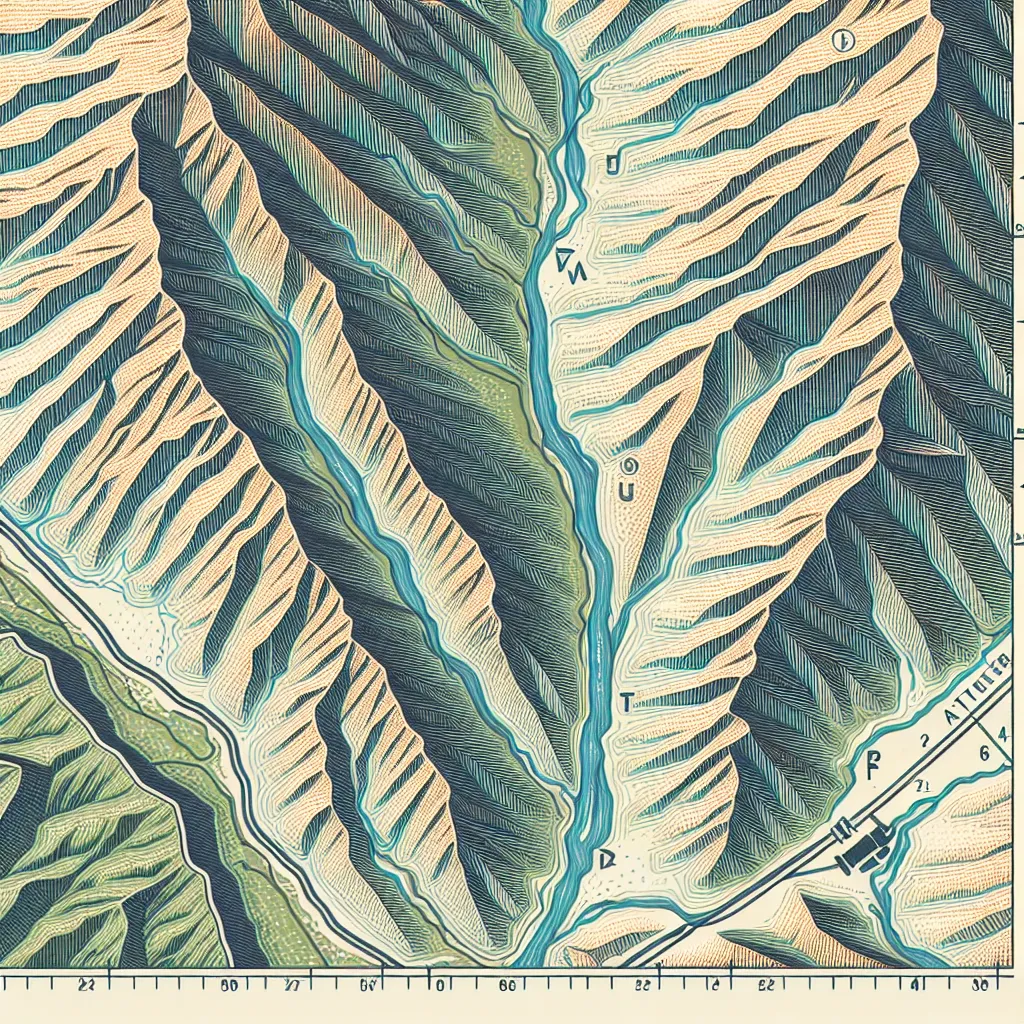
A topographic map is a detailed, accurate graphic representation of features that appear on the Earth's surface. Here are some key aspects and uses of topographic maps: 1. **Elevation and Contour Lines**: - **Contour Lines**: These are lines that connect points of equal elevation. They indicate the height of land above sea level. - **Contour Interval**: The difference in elevation between adjacent contour lines. It’s consistent throughout the map. - **Close Lines**: Indicate steep terrain. - **Wide Lines**: Suggest gentle slopes or flat land. 2. **Natural Features**: - Depicts mountains, valleys, plains, lakes, rivers, and more. - Useful for outdoor activities like hiking, hunting, or camping where knowing the terrain is crucial. 3. **Man-made Features**: - Includes roads, buildings, urban developments, railways, and other infrastructure. - Essential for planning construction projects, urban planning, and navigation. 4. **Terrain Representation**: - Shows the shape and form of the Earth's surface with considerable detail. - Helps in understanding landscape features and elevations. 5. **Grid System**: - Often includes a coordinate system such as latitude and longitude or UTM (Universal Transverse Mercator), aiding in precise location identification. - Helpful for GPS navigation and cross-referencing with other maps. 6. **Legends and Symbols**: - Contains a legend explaining symbols and scale. - Symbols represent various features like forested areas, water bodies, and specific landmarks. ### Uses of Topographic Maps: 1. **Outdoor Recreation**: - Hiking, backpacking, camping, climbing, and fishing. 2. **Urban and Regional Planning**: - Assessing potential land use, zoning, infrastructure planning, and environmental management. 3. **Environmental and Earth Sciences**: - Studying geological formations, analyzing watershed and erosion patterns, and planning conservation efforts. 4. **Military Operations**: - Planning and executing maneuvers, understanding terrain for tactical advantages, and setting up strategic positions. 5. **Civil Engineering**: - Planning roads, bridges, tunnels, and other infrastructure by understanding the terrain. ### How to Read a Topographic Map: 1. **Identify the Contour Lines**: - Look for lines that form shapes indicative of the terrain (circles, lines, etc.). 2. **Understand the Contour Interval**: - Check the map’s legend or marginal information for the interval and use it to calculate elevation differences. 3. **Interpret the Terrain**: - Use the patterns of the contour lines to visualize the 3D shape of the land. U-shaped contours often represent valleys, while concentric circles typically indicate hills or mountains. 4. **Note the Scale**: - Ensure that you understand the scale to accurately interpret distances on the map. 5. **Use the Grid System**: - Locate coordinates or features using the grid. If you are new to using topographic maps, starting with some practice in a familiar area can help you get acclimated to reading the contour lines and understanding the represented features.
Think your answer is better than the AI's? Post it below.
Other Most Relevant Posts:
Question Tags
If you want your question answered by an AI, click here.




Post your own comment: