Ask AI on The Internet
Question: a) Discuss briefly why there appear to be differences in RF values under saturated and unsaturated conditions of tlc
Thin layer chromatography (TLC) is a crucial technique in analytical chemistry used to separate and identify compounds within a mixture. One important aspect of TLC experiments is the Rf (retardation factor or retention factor) value, which is a measure of how far a compound travels up the TLC plate relative to the solvent front. Here are some reasons why Rf values might differ under saturated and unsaturated conditions: ### Saturated vs. Unsaturated Conditions 1. **Saturated Conditions:** - In TLC, a saturated environment is typically achieved by placing a filter paper soaked in solvent inside the development chamber. This creates an atmosphere saturated with solvent vapors. - Under these conditions, the TLC plate is exposed to a consistent solvent vapor environment, which can reduce the rate at which the solvent evaporates from the plate. - This results in more uniform and reproducible movement of the solvent front up the plate, leading to more consistent Rf values. 2. **Unsaturated Conditions:** - In contrast, an unsaturated environment lacks this solvent vapor equilibrium. The TLC plate is exposed to the ambient atmosphere, which is not saturated with solvent vapor. - The solvent evaporates more quickly from the plate in unsaturated conditions, leading to less uniform solvent migration and potentially inconsistent Rf values. - More rapid solvent evaporation can result in a less effective partitioning of compounds between the stationary phase (the TLC plate) and the mobile phase (the solvent), leading to variability in how far different compounds travel. ### Specific Reasons for Rf Differences 1. **Evaporation Effects:** - In unsaturated conditions, faster evaporation of the solvent can cause irregularities in the solvent front and inconsistent interaction between the stationary and mobile phases. - These irregularities can lead to differences in Rf values for the same compound compared to when the TLC run is done in a saturated environment. 2. **Solvent Polarity and Interaction:** - Solvent vapors in a saturated chamber can interact with the stationary phase, possibly altering its characteristics slightly (such as making it slightly more polar if the solvent is polar). - This can influence the interaction between the stationary phase and the compounds being analyzed, thus affecting the Rf values. 3. **Uniformity of Solvent Front:** - A more uniform solvent front in saturated conditions ensures that all spots on the TLC plate travel the same distance, enhancing reproducibility and accuracy in Rf measurements. - Without saturation, the solvent front may not be as even, leading to variability in the distances traveled by different spots, hence affecting Rf values. ### Practical Considerations - **Reproducibility:** - For reproducible and reliable Rf values, performing TLC under saturated conditions is usually recommended. - This ensures that solvent migration and compound interactions are more consistent. - **Experimental Setup:** - Different experimental setups might necessitate tuning the environment depending on the desired resolution and the nature of the compounds analyzed. In summary, the differences in Rf values between saturated and unsaturated conditions arise from how solvent vapor equilibrium (or the lack thereof) impacts the solvent front's uniformity and the interaction dynamics between the stationary and mobile phases. Saturated conditions typically offer more reliable and consistent Rf values compared to unsaturated conditions, where faster solvent evaporation can lead to variability in the TLC results.
Think your answer is better than the AI's? Post it below.
Other Most Relevant Posts:
 Ask AI: a) Discuss briefly why there appear to be differences in RF values under saturated and unsaturated conditions of TLC.
Ask AI: a) Discuss briefly why there appear to be differences in RF values under saturated and unsaturated conditions of TLC.
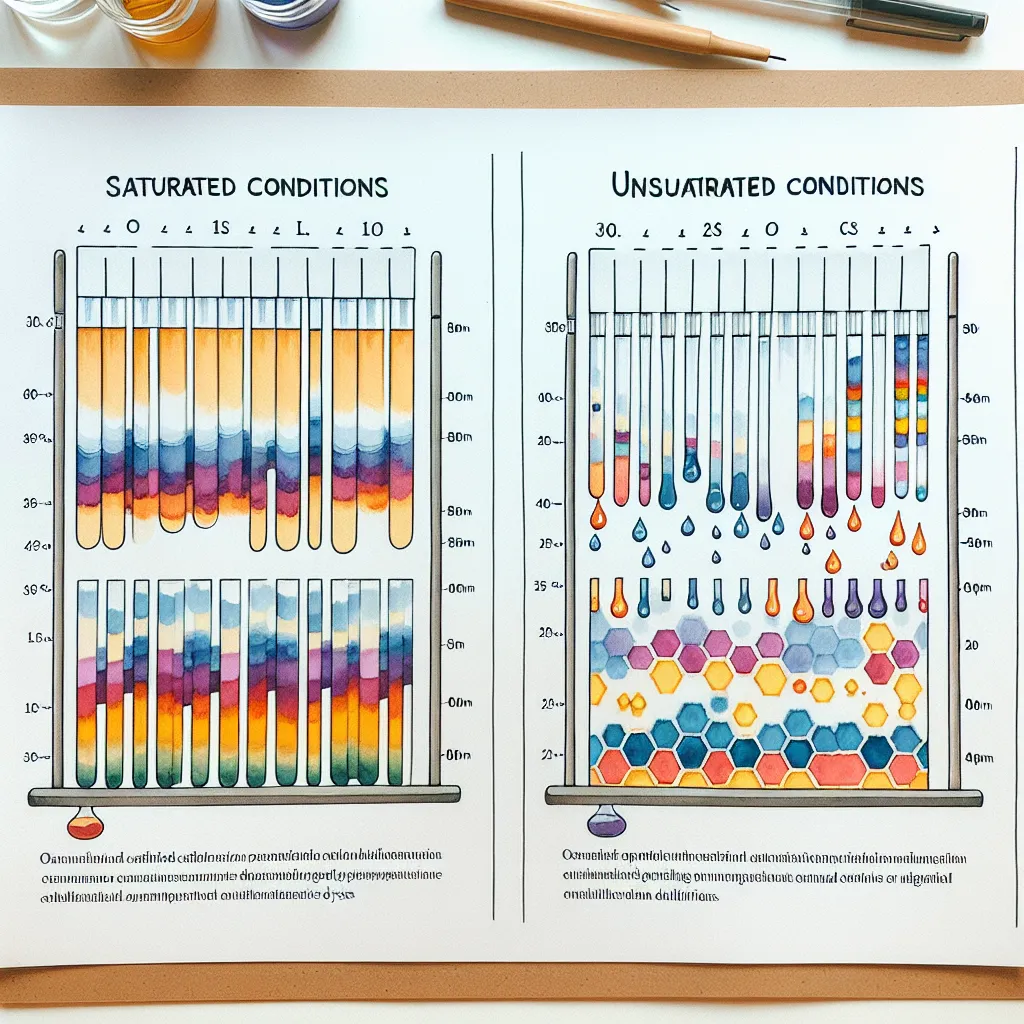 Ask AI: Discuss the separation of organic dyes under two different set of conditions: Saturated and unsaturated using THIN LAYER CHROMATOGRAPHY
Ask AI: Discuss the separation of organic dyes under two different set of conditions: Saturated and unsaturated using THIN LAYER CHROMATOGRAPHY
 Title: Exploring the Possibility of Using Eluent Solvent Mixtures in the Unsaturated Mode in Thin Layer Chromatography (TLC)
Title: Exploring the Possibility of Using Eluent Solvent Mixtures in the Unsaturated Mode in Thin Layer Chromatography (TLC)
Question Tags
If you want your question answered by an AI, click here.



Post your own comment: