Ask AI on The Internet
Question: Describe the following elements of Movement West 17) Land Grants – 18) Transcontinental Railroad – 19) Open Range – 20) Vaqueros – 21) Cattle Drives - 22) Cow Towns - 23) Homestead Act – 24) Exodusters - 25) Great Migration - 26) Barbed Wire - 27) Oklahoma Sooners - 28) Who is laying the Railroad tracks? - 29) Dust Bowl - 30) Expansionist - 31) Gadsden Purchase - 32) Compromise of 1850 - 33) Mass Transit - 34) Suburbs - 35) Urbanization - Short Answer Questions: Need to Answer Both Questions on the Test Describe the life of a miner in California during the Gold Rush. Who was moving to California and why? What were mining camps like? Discuss the eventual growth of towns out west following the Gold Rush. Discuss the conditions that led people to migrate from rural areas to urban regions. What changes happening on farms forced people away? Why were urban areas so attractive to people looking for work? Describe conditions of these growing urban areas. Short Answers Only
Sure, here are the short descriptions of each element: 17) **Land Grants** – Parcels of land given by the government to encourage development, exploration, and settlement, often used for building railroads, colleges, or farming. 18) **Transcontinental Railroad** – A major rail line built in the 1860s that connected the Eastern United States with the Western United States, facilitating commerce, communication, and travel. 19) **Open Range** – Large areas of public land where cattle roamed freely and grazed without fence restrictions, critical to the cattle industry before fencing became widespread. 20) **Vaqueros** – Skilled horsemen and cattle herders of Mexican origin, who influenced the American cowboy culture, techniques, and style. 21) **Cattle Drives** – The process of moving large herds of cattle from Texas to railheads in Kansas, where they were shipped east to market. 22) **Cow Towns** – Towns that sprang up at the end of cattle drives where cattle were sold and shipped east; notable examples include Dodge City and Abilene. 23) **Homestead Act** – Legislation passed in 1862 that provided 160 acres of public land for a small fee to any adult citizen who agreed to farm the land for at least five years. 24) **Exodusters** – African Americans who migrated from the Southern United States to Kansas in the late 19th century seeking better opportunities and escaping racial oppression. 25) **Great Migration** – The large-scale movement of African Americans from the rural South to urban areas in the North between 1916 and 1970 seeking industrial jobs and escaping Jim Crow laws. 26) **Barbed Wire** – An inexpensive fencing material invented in 1874 by Joseph Glidden, which revolutionized farming and ranching by allowing farmers to fence off their land and control livestock. 27) **Oklahoma Sooners** – Settlers who illegally entered and settled on land in present-day Oklahoma before the official start of the land rush in 1889. 28) **Who is laying the Railroad tracks?** – Predominantly immigrant laborers, including many Chinese immigrants in the West and Irish immigrants in the East, along with other disadvantaged groups. 29) **Dust Bowl** – Severe dust storms during the 1930s that severely damaged the ecology and agriculture of the US and Canadian prairies, leading to widespread displacement. 30) **Expansionist** – Advocates of territorial expansion, promoting the belief that a nation should grow its land area for increased power, resources, and influence. 31) **Gadsden Purchase** – An 1853 purchase by the United States of land from Mexico (present-day southern Arizona and southwestern New Mexico) to facilitate a southern transcontinental railroad route. 32) **Compromise of 1850** – A set of laws passed to defuse a political confrontation between slave and free states regarding territories acquired during the Mexican-American War. 33) **Mass Transit** – Public transportation systems like buses, trains, and subways designed to move large numbers of people within urban areas efficiently. 34) **Suburbs** – Residential areas on the outskirts of cities that grew rapidly, especially post-World War II, offering more space and a suburban lifestyle. 35) **Urbanization** – The process by which more of a population comes to live in cities and towns, accelerating with industrialization and the need for labor in urban factories. **Short Answer Questions**: **1. Describe the life of a miner in California during the Gold Rush. Who was moving to California and why? What were mining camps like? Discuss the eventual growth of towns out west following the Gold Rush.** Miners during the Gold Rush faced arduous conditions, working long hours with uncertain success. People moved to California from various parts of the U.S. and the world, drawn by the opportunity to strike it rich. Mining camps were often rough, temporary settlements with minimal facilities and high crime rates. Over time, successful mining camps grew into permanent towns, fostering trade, businesses, and communities. **2. Discuss the conditions that led people to migrate from rural areas to urban regions. What changes happening on farms forced people away? Why were urban areas so attractive to people looking for work? Describe conditions of these growing urban areas.** People migrated from rural to urban areas due to agricultural mechanization, which reduced the demand for farm labor, and economic hardships like the Dust Bowl. Urban areas offered more job opportunities in factories and industries. However, the rapid urban growth led to overcrowded living conditions, poor sanitation, and inadequate infrastructure, presenting new social challenges.
Think your answer is better than the AI's? Post it below.
Other Most Relevant Posts:
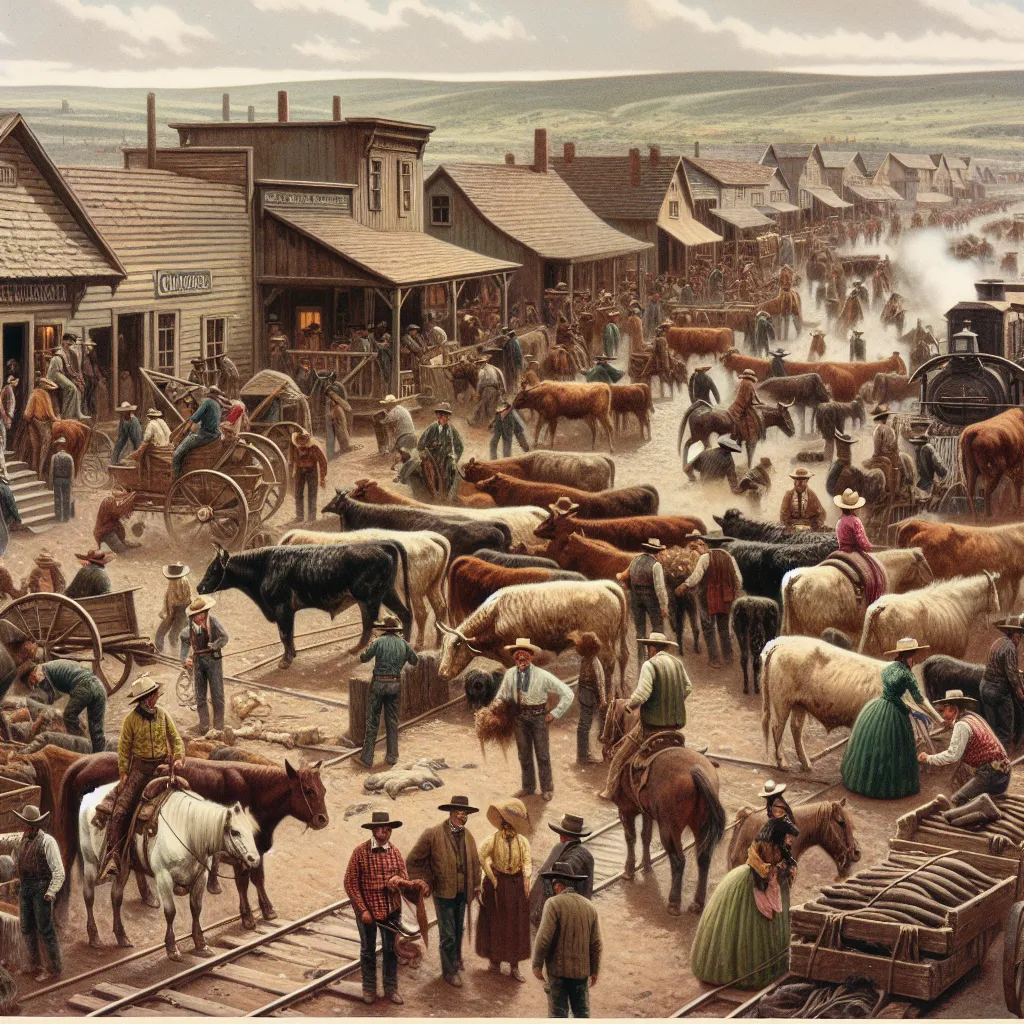
 17) Government Land Grants
18) Transcontinental Railroad's Impact
19) The Open Range System
20) Influence of Vaqueros
21) Challenges of Cattle Drives
22) Rise of Cow Towns
23) The Homestead Act's
17) Government Land Grants
18) Transcontinental Railroad's Impact
19) The Open Range System
20) Influence of Vaqueros
21) Challenges of Cattle Drives
22) Rise of Cow Towns
23) The Homestead Act's
 52) Tenement Housing: Poor Conditions in Urban Dwellings
53) Sand Creek Massacre: Deadly Attack on Native American Village
54) Battle of Wounded Knee: Violent Confrontation with Sioux
55) Dust Bo
52) Tenement Housing: Poor Conditions in Urban Dwellings
53) Sand Creek Massacre: Deadly Attack on Native American Village
54) Battle of Wounded Knee: Violent Confrontation with Sioux
55) Dust Bo
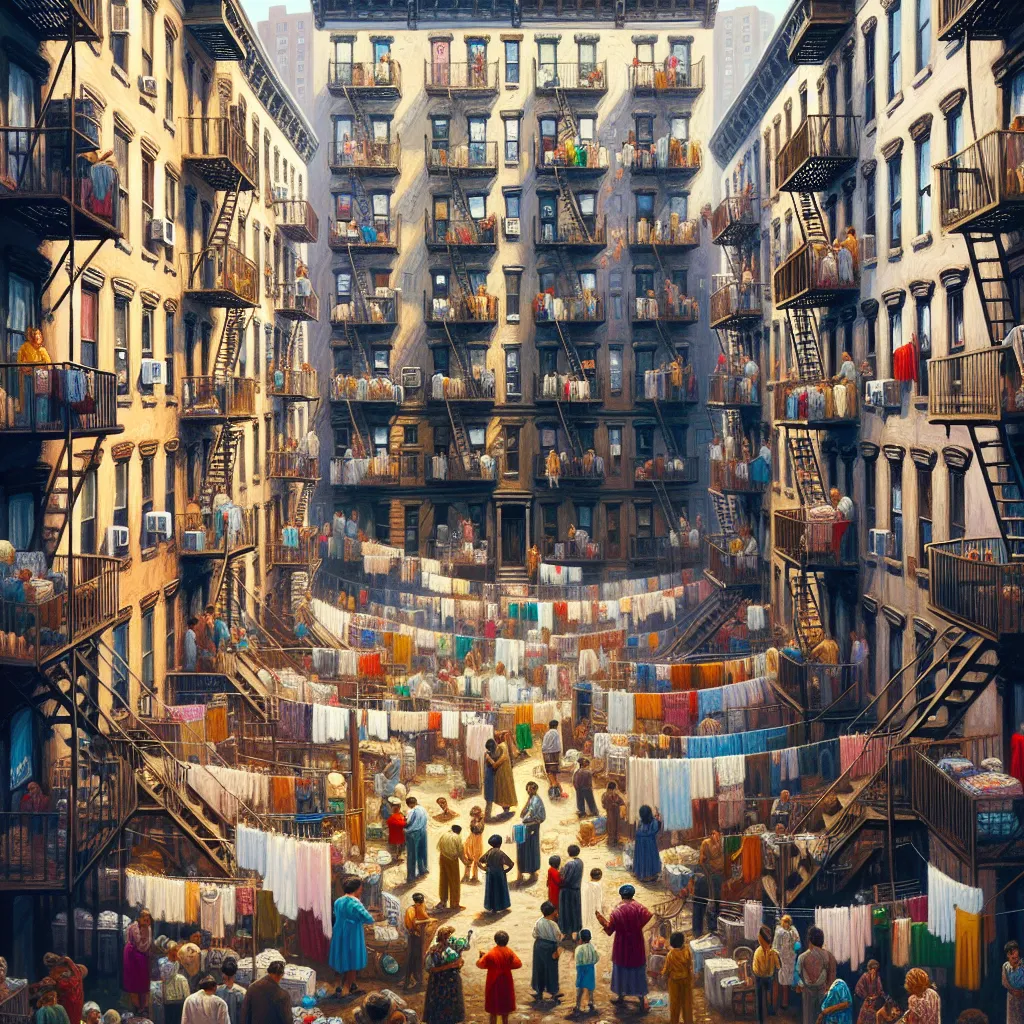 1. Tenement Housing in the Shadow of Industrialization
2. The Sand Creek Massacre: A Tragic Chapter in History
3. Battle of Wounded Knee: A Broken Treaty's Final Confrontation
4. Dust Bowl Migran
1. Tenement Housing in the Shadow of Industrialization
2. The Sand Creek Massacre: A Tragic Chapter in History
3. Battle of Wounded Knee: A Broken Treaty's Final Confrontation
4. Dust Bowl Migran
 61) Urbanization Explained
62) The Concept of Steerage
63) Jane Addams and Settlement Houses
64) Understanding Nativists
65) Push and Pull Factors
66) Ellis Island vs. Angel Island
67) Americ
61) Urbanization Explained
62) The Concept of Steerage
63) Jane Addams and Settlement Houses
64) Understanding Nativists
65) Push and Pull Factors
66) Ellis Island vs. Angel Island
67) Americ
Question Tags
If you want your question answered by an AI, click here.


Post your own comment: